Software
I have developed a technical computer program using the Python programming language to reduce calculation time and improve accuracy. The program is designed to solve complex calculations efficiently and effectively, allowing for faster and more accurate results. With my expertise in Python programming, I have developed a solution that is both user-friendly and highly effective for a wide range of technical applications.
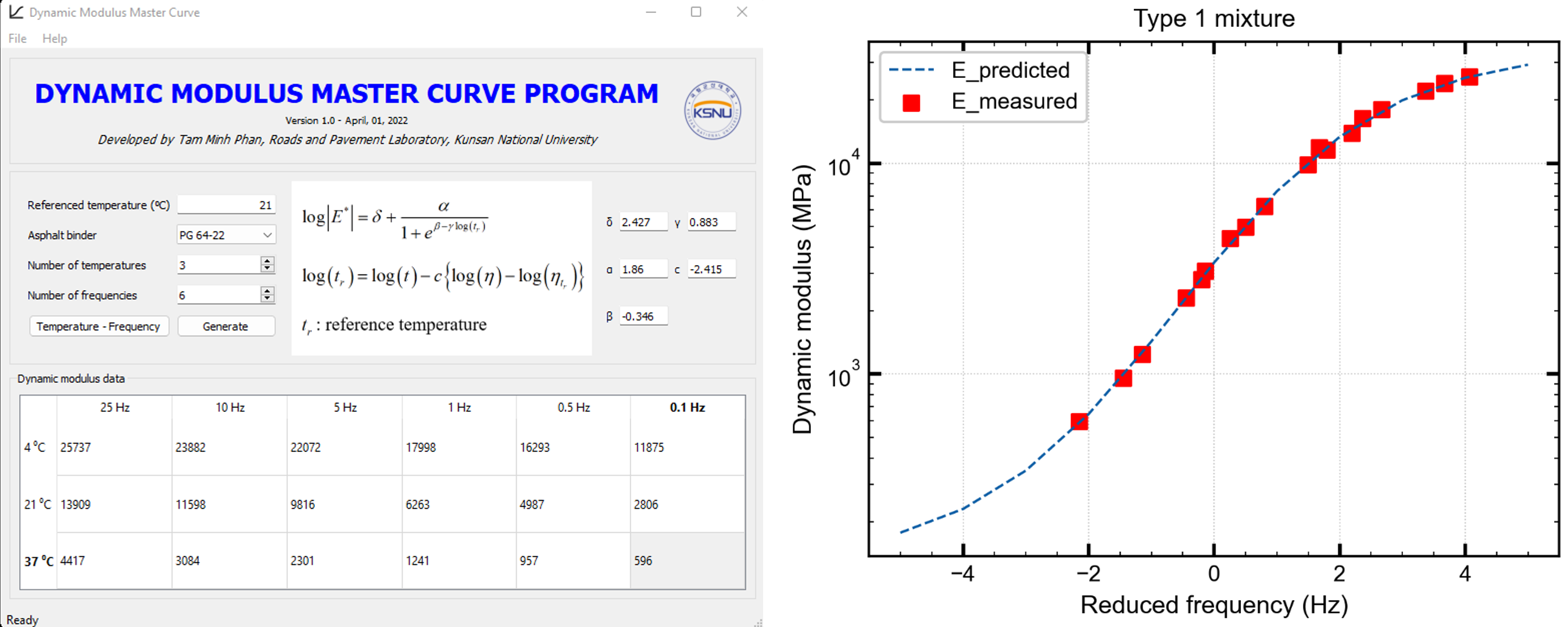
Dynamic Modulus Master Curve
The dynamic modulus master curve is a mathematical model used to predict the stiffness of asphalt concrete under different temperature and loading conditions. It combines laboratory testing and computational methods to generate a comprehensive picture of the material’s behavior, helping engineers design more durable and reliable asphalt pavements.
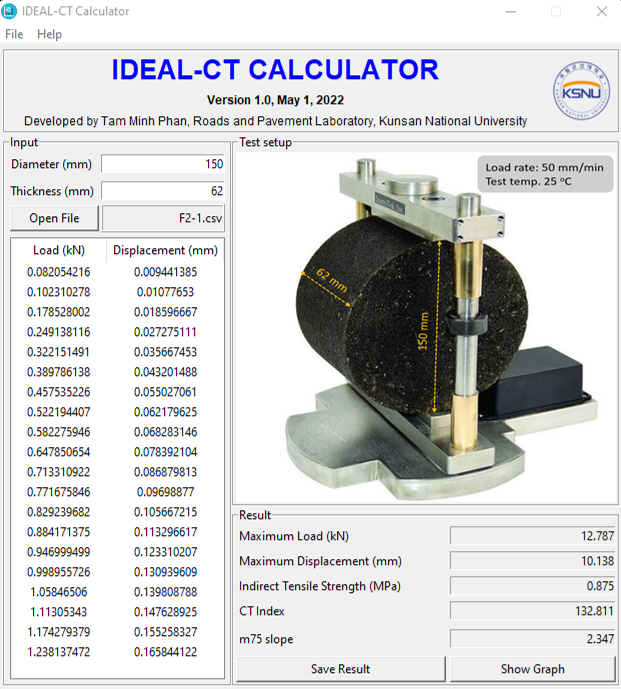
IDEAL-CT Calculator
IDEAL-CT (Indirect Tensile Asphalt Cracking Test) is a reliable design procedure for concrete pavements that can resist fatigue, reflective, top-down, and low-temperature cracking. The CTIndex (Cracking Tolerance Index) is a measure of a pavement’s ability to resist cracking, calculated based on pavement properties, traffic loads, and environmental conditions. Unlike some machines that use only the maximum load, the calculation of the CTIndex requires the entire load versus displacement curve, which is a common requirement for tests that evaluate the mechanical properties of materials.
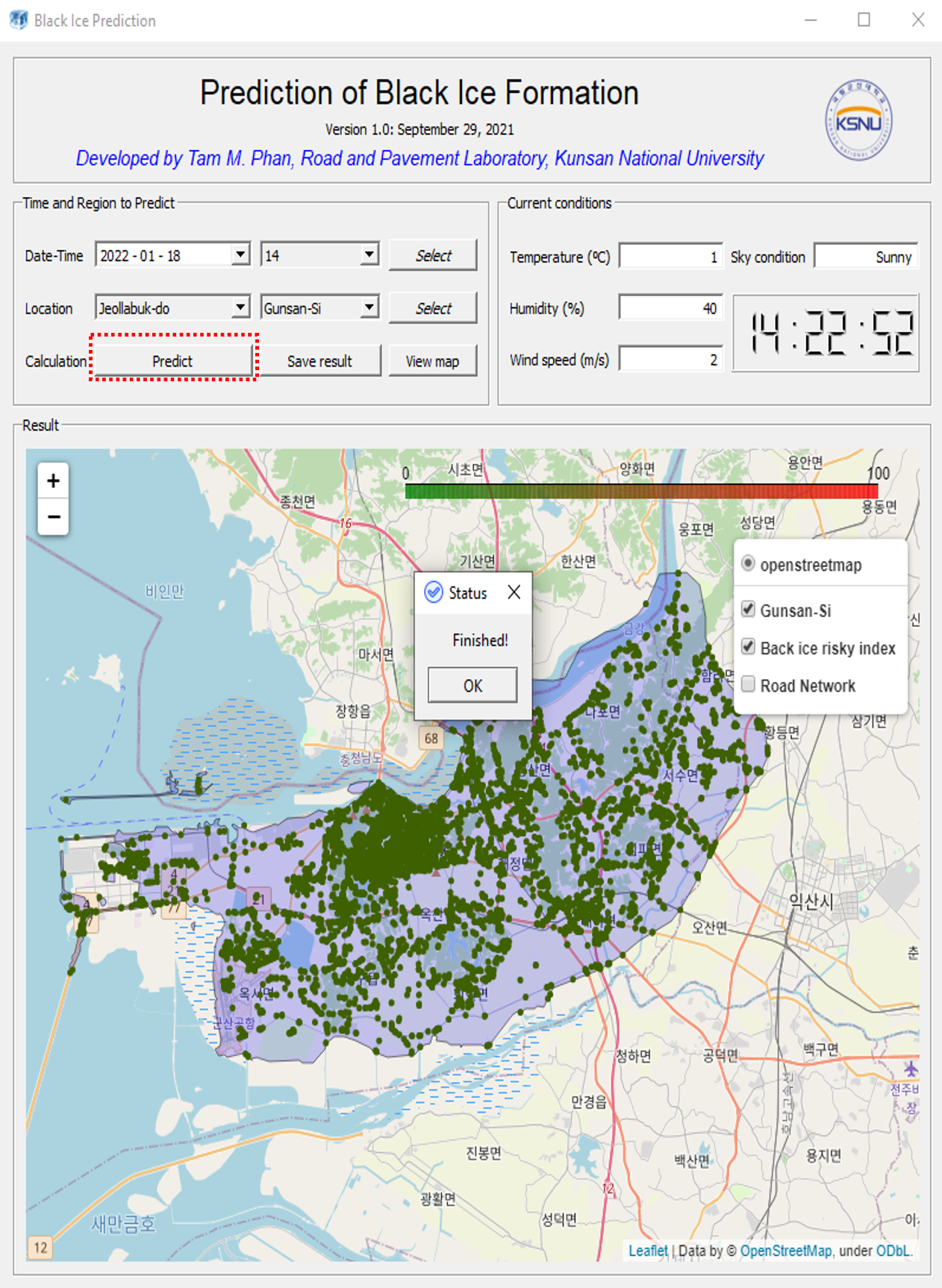
Black ice prediction program
A black ice prediction program is a computerized tool that uses data from weather forecasts, pavement temperature sensors, and other sources to predict the formation of black ice on roadways. Black ice is a thin, transparent layer of ice that forms on pavement surfaces and can cause hazardous driving conditions. The prediction program can help transportation agencies and maintenance crews make informed decisions about when and where to apply anti-icing or de-icing treatments to prevent or mitigate the impact of black ice on road safety.
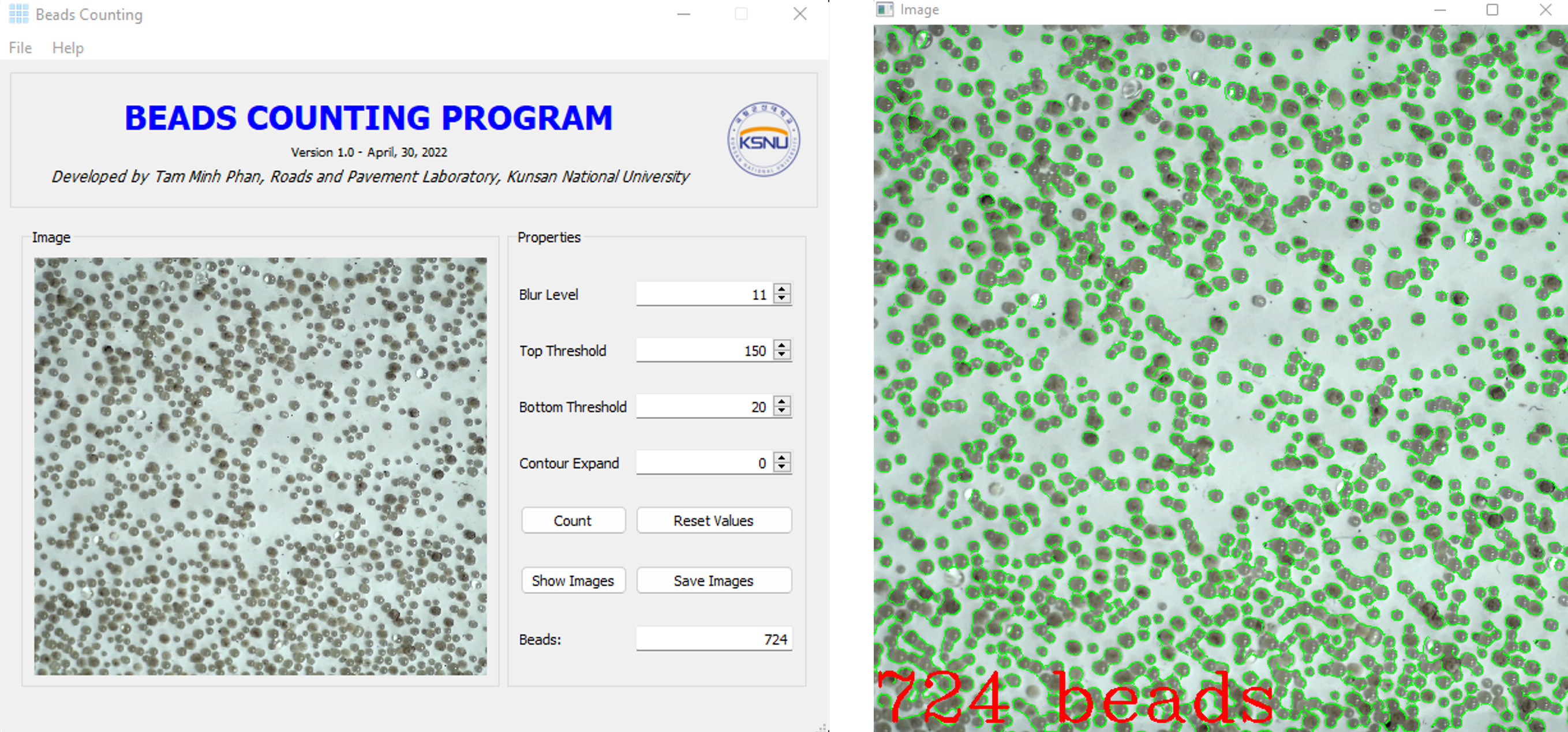
Beads Couting Program
A beads counting program is a computerized tool used to analyze and quantify the number and size distribution of microscopic beads or particles in a sample. This type of program is commonly used in research, quality control, and manufacturing processes, where accurate and precise measurement of particle size and concentration is critical. Beads counting programs typically use image processing algorithms and software to analyze images of the sample taken under a microscope or other imaging system
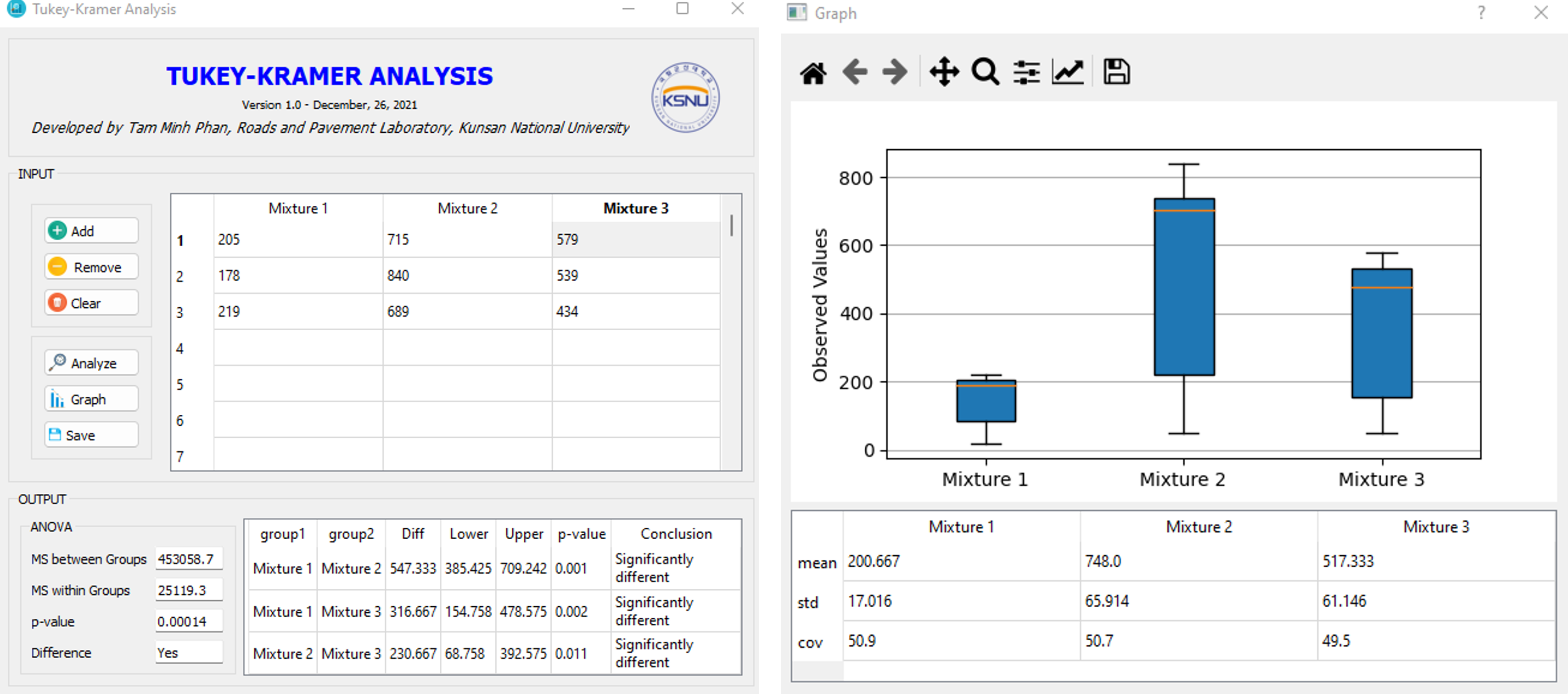
Tukey-Kramer post-hoc Analysis
The Tukey-Kramer post-hoc analysis, also known as the Tukey’s range test, is a statistical method used to determine the significant differences between multiple groups in an experiment after conducting an ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) test. The Tukey-Kramer test compares the means of all possible pairs of groups and calculates the minimum significant difference (MSD) needed to declare a significant difference between them. If the difference between two groups exceeds the MSD, then those groups are considered significantly different at a certain level of confidence (usually 95% or 99%). The Tukey-Kramer test is a conservative post-hoc test, meaning that it controls the overall error rate by adjusting the significance level based on the number of pairwise comparisons made. This test is commonly used in the fields of biology, psychology, and social sciences, among others, to identify significant differences between experimental groups.